Structure and Properties
HTD1801, a first-in-class new molecular entity (NME), is an ionic salt of berberine and ursodeoxycholic acid that was engineered to exert the biological activities of its active components.

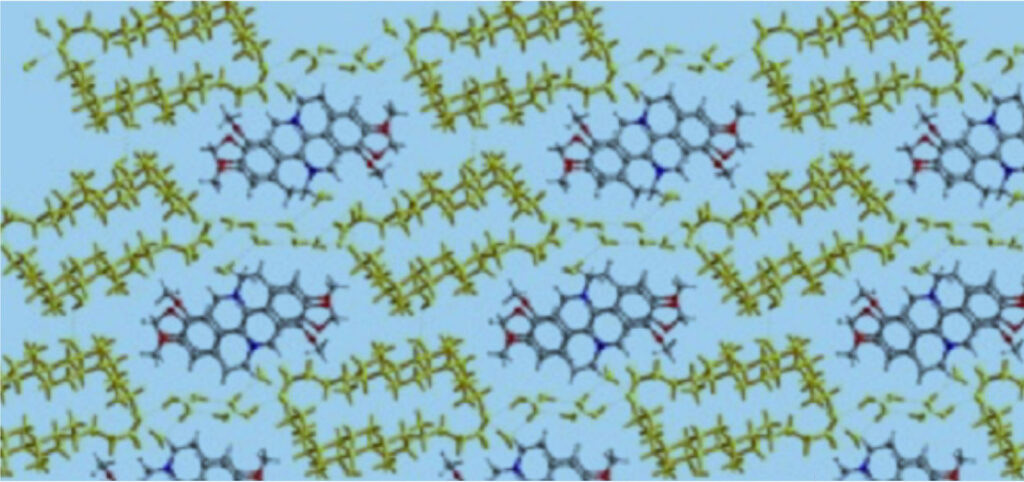
HTD1801, a first-in-class new molecular entity (NME), is an ionic salt of berberine and ursodeoxycholic acid that was engineered to exert the biological activities of its active components.


HTD1801 is a potentially first-in-class orally delivered anti-inflammatory metabolic modulator being developed for the treatment of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) diseases.
Our lead compound, HTD1801, provides dual mechanisms of action – AMP kinase activation and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition.
These two key mechanistic pathways have been associated with improvements in glucose metabolism, insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, hepatic inflammation, and gut microbiome. These unique dual mechanism has the potential to address CKM at its root, providing a comprehensive treatment for the multifaceted nature of complex metabolic diseases, and delivering comprehensive benefits to patients with CKM.
These two key mechanistic pathways have been associated with improvements in glucose metabolism, insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, hepatic inflammation, and gut microbiome. This unique dual mechanism has the potential to address CKM at its root, providing a comprehensive treatment approach for the multifaceted nature of complex metabolic diseases, and delivering comprehensive benefits to patients with CKM.
Inflammation
Steatosis
Fibrosis
Cholestasis
Cholangitis
Body Weight
Inflammation
Atherogenic Lipids
Oxidative Stress
Glucose Clearance
Harmful Microbiota
Beneficial Microbiota
Insulin Resistance
Glycemic Control
Our priority in the clinic is advancing our lead candidate HTD1801 in cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) diseases driven by insulin resistance and chronic inflammation.
Clinical trials in patients with T2DM, MASH and PSC have been completed or are ongoing, evaluating the effects of HTD1801 on liver fat content, markers of liver fibrosis, markers of liver inflammation and injury, as well as metabolic changes such as reductions in elevated lipids (LDL-C and triglycerides), improvements in HbA1c and fasting glucose and weight loss.
References